SHAREWARE
(lets share it!)
This blog consist of intresting facts from all over the world on technology,marketing,sea life and latest news.
I regularly update mt blog and keep my readers updated and share lots of information.
1.PUFFERFISH:
Pufferfish are generally believed to be the second-most poisonous vertebrates in the world, after the golden poison frog. Certain internal organs, such as liver, and sometimes the skin, contain tetrodotoxin .The puffer's unique and distinctive natural defenses help compensate for its slow locomotion. It moves by combining pectoral, dorsal, anal, and caudal fins. This makes it highly maneuverable, but very slow, and therefore a comparatively easy predation target. Its tail fin is mainly used as a rudder, but it can be used for a sudden evasive burst of speed that shows none of the care and precision of its usual movements. The puffer's excellent eyesight, combined with this speed burst, is the first and most important defense against predators.
Its backup defense mechanism, used if successfully pursued, is to fill its extremely elastic stomach with water (or air when outside the water) until it is much larger and almost spherical in shape. Even if they are not visible when the puffer is not inflated, all puffers have pointed spines, so a hungry predator may suddenly find itself facing an unpalatable, pointy ball rather than a slow, tasty fish. Predators which do not heed this warning (or which are "lucky" enough to catch the puffer suddenly, before or during inflation) may die from choking, and predators that do manage to swallow the puffer may find their stomachs full of tetrodotoxin, making puffers an unpleasant, possibly lethal, choice of prey. This neurotoxin is found primarily in the ovaries and liver, although smaller amounts exist in the intestines and skin, as well as trace amounts in muscle. It does not always have a lethal effect on large predators, such as sharks, but it can kill humans.
OUTERNET
The Outernet is a global networking project currently under development by the Media Development Investment Fund (MDIF), a United States-based non-profit organization established in 1995 by Saša Vučinić and Stuart Auerbach. The Outernet's goal is to provide free access to internet data through Wi-Fi, made available effectively to all parts of the world.
The project would involve using datacasting and User Datagram Protocol through hundreds of CubeSats measuring 10 cm (3.9 in) each. Wi-Fi enabled devices would communicate with the satellites in their region, which in-turn communicate with other satellites and ground-based networks, thus forming the global network.
The network would initially support only one-way traffic, with two-way traffic being implemented once adequate funding is raised. Initial prototype satellite deployment is planned for June 2014, with the final deployment run scheduled for mid-2015. According to MDIF, the initial content access includes international and local news, crop prices for farmers, Teachers Without Borders, emergency communications such as disaster relief, applications and content such as Ubuntu, movies, music games, and Wikipedia in its entirety.
"There isn't a lot of raw research that is being done here; much of what is being described has already been proven by other small satellite programs and experiments," stated Project Lead Syed Karim. "There's really nothing that is technically impossible to this."
MDIF plans to formally request NASA to use the International Space Station to test their technology in September 2014. Manufacturing and launching of satellites would begin in early 2015, and Outernet is planned to begin broadcasting in June 2015. India based "Spacify Inc." is a private non-profit company by Silicon Valley based technocrat and entrepreneur Siddharth Rajhans along with Space debris mitigation expert Sourabh Kaushal, which is privately working on using this technology to provide global free Wi-Fi access.
GOOGLE LOON
Project Loon is a research and development project being developed by Google with the mission of providing Internet access to rural and remote areas. The project uses high-altitude balloons placed in the stratosphere at an altitude of about 20 mi (32 km) to create an aerial wireless network with up to 3G-like speeds.Because of the project's seemingly outlandish mission goals, Google dubbed it "Project Loon".
The balloons are maneuvered by adjusting their altitude to float to a wind layer after identifying the wind layer with the desired speed and direction using wind data from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Users of the service connect to the balloon network using a special Internet antenna attached to their building. The signal travels through the balloon network from balloon to balloon, then to a ground-based station connected to an Internet service provider (ISP), then onto the global Internet. The system aims to bring Internet access to remote and rural areas poorly served by existing provisions, and to improve communication during natural disasters to affected regions.Key people involved in the project include Rich DeVaul, chief technical architect, who is also an expert on wearable technology; Mike Cassidy, a project leader; and Cyrus Behroozi, a networking and telecommunication lead.
what is technique?
The technology designed in the project could allow countries to avoid using expensive fiber cable that would have to be installed underground to allow users to connect to the Internet. Google feels this will greatly increase Internet usage in developing countries in regions such as Africa and Southeast Asia that can't afford to lay underground fiber cable.
The high-altitude polyethylene balloons fly around the world on the prevailing winds (mostly in a direction parallel with lines of latitude, i.e. east or west). Solar panels about the size of a card table that are just below the free-flying balloons generate enough electricity in four hours to power the transmitter for a day and beam down the Internet signal to ground stations. These ground stations are spaced about 100 km (62 mi) apart, or two balloon hops, and bounce the signal to other relay balloons that send the signal back down. This makes Internet access available to anyone in the world who has a receiver and is within range of a balloon. Currently, the balloons communicate using unlicensed 2.4 and 5.8 GHz ISM bands,and Google claims that the setup allows it to deliver "speeds comparable to 3G" to users. It is unclear how technologies that rely on short communications times (low latency pings), such as VoIP, might need to be modified to work in an environment similar to mobile phones where the signal may have to relay through multiple balloons before reaching the wider Internet.
The first person to connect to the "Google Balloon Internet" after the initial test balloons were launched into the stratosphere was a farmer in the town of Leeston, New Zealand, who was one of 50 people in the area around Christchurch who agreed to be a pilot tester for Project Loon. The New Zealand farmer lived in a rural location that couldn't get broadband access to the Internet, and had used a satellite Internet service in 2009, but found that he sometimes had to pay over $1000 per month for the service.
share my dabba
Share My Dabba is an initiative to get food left uneaten in dabbas to hungry street children, using just a Share sticker and the dabbawala network.Conceived by McCann Mumbai, the initiative is a joint effort between Happy Life Welfare Society and The Dabbawala Foundation.
tribute to indian classic advertisements..jingles
share my dabba
tribute to indian classic advertisements..jingles
AIB collaborates with Voctronica to pay tribute to the era of advertising that defined our childhood. We recommend you listen with your headphones on!
Check out the edited version of the song on our main channel at: http://bit.ly/1mQN1OM & guess the names all of ads and leave a comment, stand a chance to win some AIB merch!
Get AIB merch on Snapdeal: http://www.snapdeal.com/brand/all-ind...
Credits:
Created by: AIB & Voctronica
Directed by: Kumar Devanshu, Tanmay Bhat
DOP: Sahirr Raza, Vivian
Assistant Directors: Junhai Nath, Karunesh Talwar
Creative Directors: Karunesh Talwar, Tanmay Bhat, Arjun Nair
Line Producer: Vikram Singh
Editor: Shashwata Dutta
Online Gfx: Rishab Malhotra
DI: QLabs
Mix: Arjun Nair
Voice Over: Ashwin Mushran
Check out the edited version of the song on our main channel at: http://bit.ly/1mQN1OM & guess the names all of ads and leave a comment, stand a chance to win some AIB merch!
Get AIB merch on Snapdeal: http://www.snapdeal.com/brand/all-ind...
Credits:
Created by: AIB & Voctronica
Directed by: Kumar Devanshu, Tanmay Bhat
DOP: Sahirr Raza, Vivian
Assistant Directors: Junhai Nath, Karunesh Talwar
Creative Directors: Karunesh Talwar, Tanmay Bhat, Arjun Nair
Line Producer: Vikram Singh
Editor: Shashwata Dutta
Online Gfx: Rishab Malhotra
DI: QLabs
Mix: Arjun Nair
Voice Over: Ashwin Mushran
coca cola campaigns
packaging(all big players are focusing now):
Product packaging plays an important role in the marketing mixPackaging plays an important role as a medium in the marketing mix, in promotion campaigns, as a pricing criterion, in defining the character of new products, as a setter of trends and as an instrument to create brand identity and shelf impact in all product groups.
new product development
www.youtube.com/watch?v=mxsDhgFGxnM
NOKIA NEW TECHNOLOGY
technology in shoes "le chal"
Coca-Cola as a part of their newcampaign have set up phone booths forSouth Asian workers in Dubai to call back home more often. The phone booth which connects the migrant workers to their families in India and Pakistan accepts Coca-Cola bottle caps as currency instead of coins. One cap is good for a three minute call to their loved ones.
The humble gesture by the company has made the workers visually happy, as is seen in the three minute ad posted on the official YouTube channel of Coca-Cola. They say they're happy and even their families back in India and Pakistan are delighted since they can contact their loved ones more often now.
packaging(all big players are focusing now):
Product packaging plays an important role in the marketing mix
Product packaging plays an important role in the marketing mixPackaging plays an important role as a medium in the marketing mix, in promotion campaigns, as a pricing criterion, in defining the character of new products, as a setter of trends and as an instrument to create brand identity and shelf impact in all product groups.
The findings of many other research projects are supplemented by the survey carried out by IRI (Information Resources Inc.), which provides information about this subject from extensive, in-depth interviews and POS polls, specifically including the issue of multisensory appeal, which is a particular trend. It also presents new arguments and evidence confirming a central conviction held by the packaging industry: that the shopper appreciates and in fact explicitly wants to receive stimulation for the buying decision he is making when standing in front of the supermarket shelf, often even preferring this to other forms of communication. He is keen to be informed and inspired, tempted and pampered by surprising and persuasive functions, emotions and sensual impressions
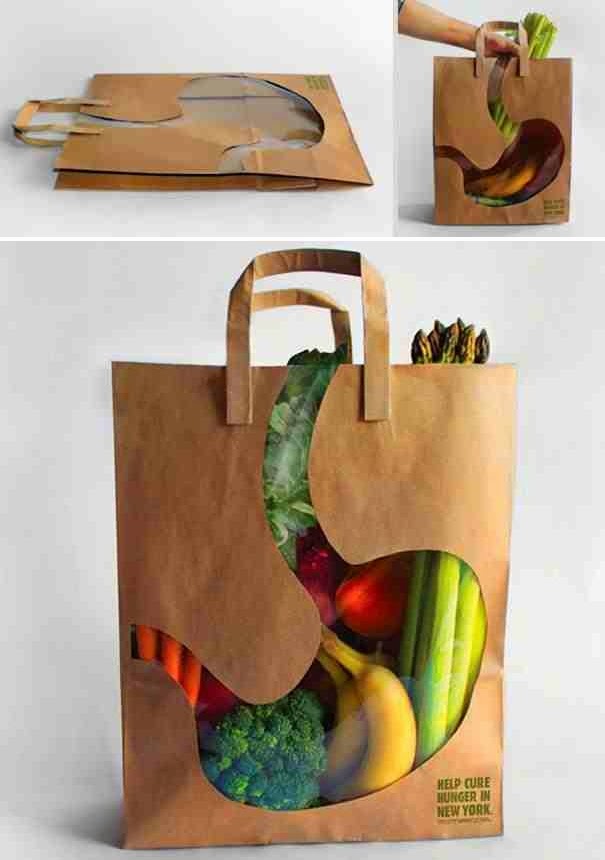
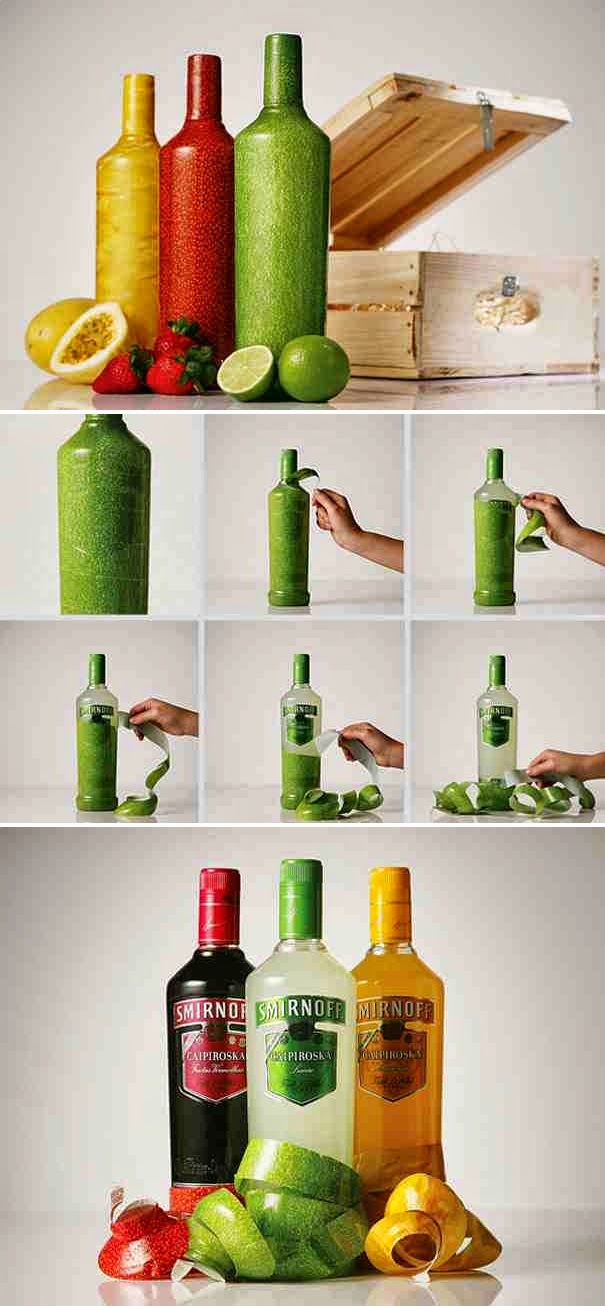
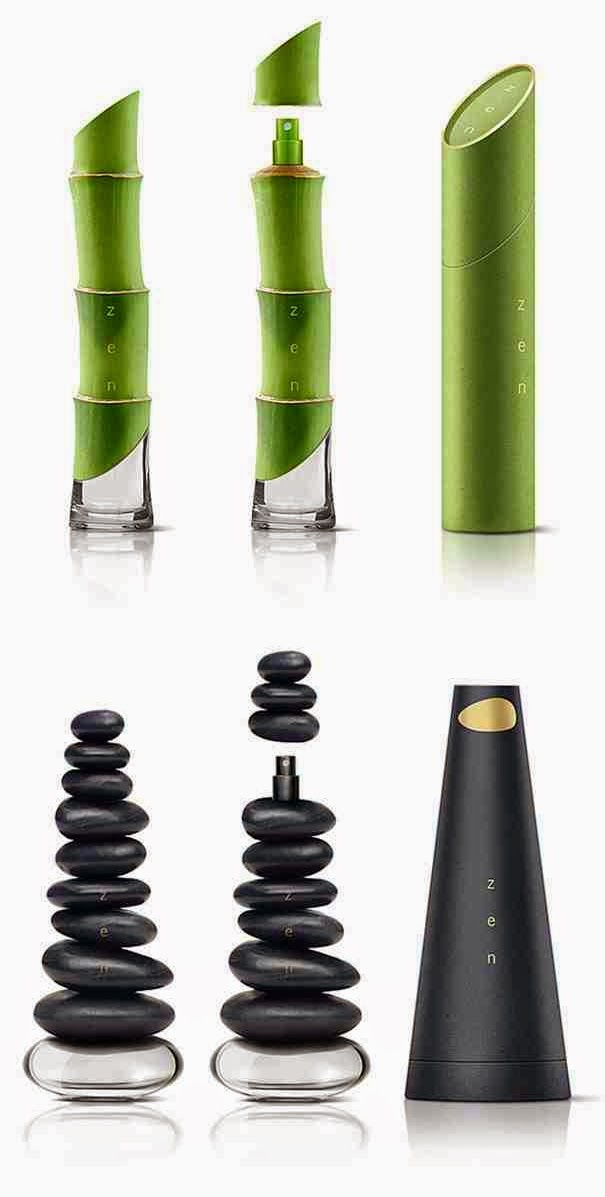
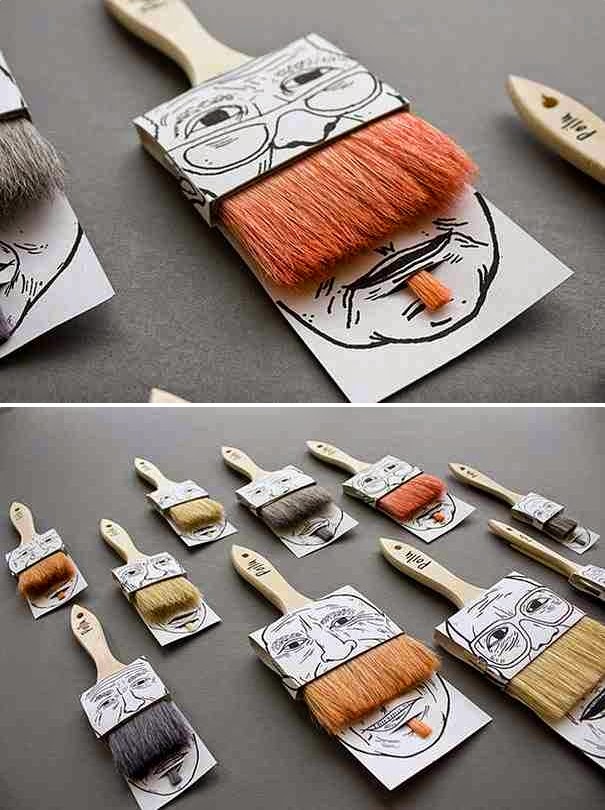
TAKE A TOUR TO BEST PACKAGING METHODS APPLIED IN SOME BRANDS:
what is npd?
There have been a number of approaches proposed for analyzing and responding to the marketing challenges of new product development. Two of these are the eight stagesprocess of Koen and a process known as the fuzzy front end.
The eight stages
- Idea Generation is often called the "NPD" of the NPD process.
- Ideas for new products can be obtained from basic research using a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities & Threats). Market and consumer trends, company's R&D department, competitors, focus groups, employees, salespeople, corporate spies, trade shows, or ethnographic discovery methods (searching for user patterns and habits) may also be used to get an insight into new product lines or product features.
- Lots of ideas are generated about the new product. Out of these ideas many are implemented. The ideas are generated in many forms. Many reasons are responsible for generation of an idea.
- Idea Generation or Brainstorming of new product, service, or store concepts - idea generation techniques can begin when you have done your OPPORTUNITY ANALYSIS to support your ideas in the Idea Screening Phase (shown in the next development step).
- Idea Screening
- The object is to eliminate unsound concepts prior to devoting resources to them.
- The screeners should ask several questions:
- Will the customer in the target market benefit from the product?
- What is the size and growth forecasts of the market segment / target market?
- What is the current or expected competitive pressure for the product idea?
- What are the industry sales and market trends the product idea is based on?
- Is it technically feasible to manufacture the product?
- Will the product be profitable when manufactured and delivered to the customer at the target price?
- Concept Development and Testing
- Develop the marketing and engineering details
- Investigate intellectual property issues and search patent databases
- Who is the target market and who is the decision maker in the purchasing process?
- What product features must the product incorporate?
- What benefits will the product provide?
- How will consumers react to the product?
- How will the product be produced most cost effectively?
- Prove feasibility through virtual computer aided rendering and rapid prototyping
- What will it cost to produce it?
- Testing the Concept may involve asking a number of prospective customers to evaluate the idea
- Develop the marketing and engineering details
- Business Analysis
- Estimate likely selling price based upon competition and customer feedback
- Estimate sales volume based upon size of market and such tools as the Fourt-Woodlock equation
- Estimate profitability and break-even point
- Beta Testing and Market Testing
- Produce a physical prototype or mock-up
- Test the product (and its packaging) in typical usage situations
- Conduct focus group customer interviews or introduce at trade show
- Make adjustments where necessary
- Produce an initial run of the product and sell it in a test market area to determine customer acceptance
- Technical Implementation
- New program initiation
- Finalize Quality management system
- Resource estimation
- Requirement publication
- Publish technical communications such as data sheets
- Engineering operations planning
- Department scheduling
- Supplier collaboration
- Logistics plan
- Resource plan publication
- Program review and monitoring
- Contingencies - what-if planning
- Commercialization (often considered post-NPD)
- Launch the product
- Produce and place advertisements and other promotions
- Fill the distribution pipeline with product
- Critical path analysis is most useful at this stage
- New Product Pricing
- Impact of new product on the entire product portfolio
- Value Analysis (internal & external)
- Competition and alternative competitive technologies
- Differing value segments (price, value and need)
- Product Costs (fixed & variable)
- Forecast of unit volumes, revenue, and profit
www.youtube.com/watch?v=mxsDhgFGxnM
NOKIA NEW TECHNOLOGY
Wearable technology is likely to be the next big thing and Nokia has sure hinted in the past that the company was interested in venturing into this field. While the mobile phone manufacturer hasn’t revealed much about its plans, Nokia has lately been on a spree of filing wearable-related patents (such as a patent for a see-though display and eye-movement tracking via a sensor).
The latest patent filing indicates that Nokia is looking into an interaction system for a near-to-eye display with the combination of a hand gesture detector and a gaze tracker (NED). It uses a camera to track the gaze of an eye, and uses a second camera to track hand gestures when movement of the eye is very slight or null.
“The invention relates to a method, comprising tracking the gaze of an eye of a user by a first camera, wherein a position of the gaze determines a place for the cursor on the screen of a near-to-eye display (NED), wherein the movement of the gaze is configured to move the cursor on the screen and when the movement of the gaze is detected to be still or moving only slightly; observing a gesture of one hand of the user by a second camera, and executing a further operation if at least one gesture of the hand is detected,” the patent filing describes.
This multi-modal interaction system looks very similar to Google Glass - a wearable computing device that Google launched back in 2012. With a head-mounted display, Google Glass makes it incredibly easy to take snapshots, videos and then share them with your friends or on favored websites. You can also read your emails, know about the weather and perform Google searches with it.
\
SHAPE SHIFTING DISPLAY
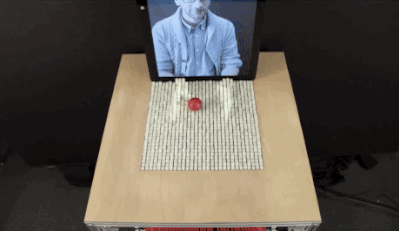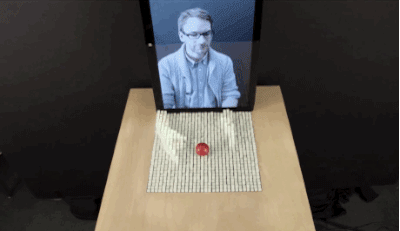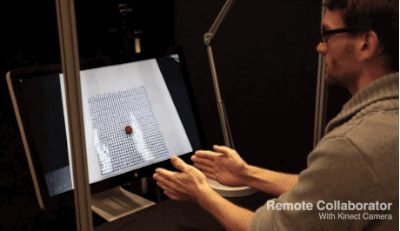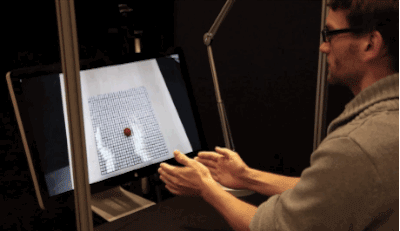
MIT has demonstrated a "Dynamic Shape Display" that can physically change shape to render 3D content. As Fast Company reports, the display is called inFORM, and it's a large surface that sits atop a series of pins, actuators, and linkages. By moving each actuator, inFORM can move the pin it's attached to up or down, allowing for a wide range of interactions.
A projector mounted above the surface provides context to the shapeshifting pins, giving them color and highlighting depth. In a video released by MIT, the table is shown moving a ball, mirroring a book, displaying 3D charts, and giving an extremely visible smartphone notification.

When used in conjunction with a Kinect sensor, inFORM gets a lot more interesting. The sensor is able to accurately map and interpret the position of 3D objects, and MIT's system uses that data to allow you to move the table's pins with just your hands. This can even work remotely, as demonstrated by the video, which shows an MIT staffer interacting with items via a video conference.
MIT says it's exploring "a number of application domains" for inFORM. Key areas of interest include 3D visualizations of CT scans and other medical uses, device interaction, and the manipulation of physical objects. It's also very interested in mapping and terrain models, which could be used by urban planners and architects to better visualize and share 3D designs. The MIT Tangible Media Group, which is responsible for inFORM's creation, says it's currently collaborating with MIT's Changing Places group to explore the possibilities for urban planners.MIT likens TUIs to a digital iceberg: just the tip of the digital content emerges "above water" into the physical realm. Moving past TUIs, the end game is Radical Atoms, a future in which "all digital information has physical manifestation ... as if the iceberg had risen from the depths to reveal its sunken mass."
technology in shoes "le chal"
It was started as a navigation aid for the visually impaired. At present people with limited or no vision depend either on walking canes, which help them detect obstructions, or seek help from friends and other people for assistance, or using voice-based navigation aids. The existing form of voice-based navigation aids can be very distracting for the blind as they mostly depend on their sense of hearing. Also, such devices are prohibitively expensive to buy.
Lechal initial prototypes got MIT TR35 Award.
The unobtrusive design of Le Chal is its most significant feature. The system comprises of a mechanism that condenses complex geographical navigational information and lets the user feel the directional and proximity information through vibrations.
AMAZING 360 degree vaccum cleaner by dyson-
After 16 years of tinkering and experimentation, Dyson is releasing its first robotic vacuum cleaner, the Dyson 360 Eye. Though iRobot released Roomba, the first autonomous sucking machine, in 2002, Dyson has been content to lay back, in hopes of ironing out some nagging limitations. “We didn’t want to put out a gimmick,” Sir James tells WIRED. He says that meant inventing a new way for the vacuum to navigate. “Accurate navigation is the key to cleaning properly,” says Dyson. “I don’t just mean in coverage, but in terms of not going over the same spot twice, because if you do that you’re wasting the battery’s power.” Put differently: Dyson didn’t want to release just any robotic vacuum cleaner. He wanted one that could do the chore as well as its human counterparts.
The Eye hinges on a 360-degree camera that views the room at a 45 degree angle and takes 30 pictures per second. Those photos become a live map of the room. To get started, the Eye undocks itself from a charging station affixed to the wall, near the floor. The robot triangulates its position in the room, finds the center, and starts spiraling outward. Once it has vacuumed 10 square feet, it relocates to clean a new patch. Infrared sensors keep the Eye aware of pets or thin table legs, but the bulk of the vacuum’s spatial smarts come from the real-time map of the room. “When you go into a room, you see there’s a corner of the table you might bump into and you know roughly how far away you are, and you can judge from it,” says Dyson. “I’m talking about the decisions you make from what you see and what you’re able to gauge. That’s precisely what our robot does with its 360-degree camera.” Once it’s covered the entire floor, it scoots back into its charging dock.
Novel as the optical mapping system may be, the vacuum still needs serious suction to be truly autonomous. “We always believed we should clean properly, and cleaning properly means you’ve got to put a lot of power and brush suction,” Dyson says. Like other recent Dyson releases, the Eye has one of the company’s proprietary digital motors—this one is a V2 that whirs at 104,000 RPM—that Dyson estimates has 20 times the force of other robot vacuums. In place of standard wheels the Eye uses treads, so the Eye can climb over ledges or door frames, sucking dust out of cracks and crevices along the way. And unlike other scuttling vacuum cleaners, the Eye’s brush bar is as wide as the body of the robot, so that everything in its path gets a full sweep.
Enthusiasts might remember the Dyson DC06, which almost launched in 2001. It had 84 sensors, needed three computers to run, and would have cost thousands of dollars. Its technique was similar to other now-popular robot vacuum cleaners that use random bounce navigation (a system of sensors and bumpers) and maps of the ceiling to make their way around a room, but do so without accurate knowledge of nearby obstacles or a memory of where they’ve been. Dyson reportedly pulled it from production because of its heavy machinery and price tag. Simply put, “we realized that a robot that relied on a lot of sensors would still not be very good,” he says.
In the years since, the company has worked on building a better alternative. Dyson, who in February invested more than $8 million in a robotics lab at Imperial College London, believes the future of robotics lies in vision-powered systems. Indeed, the technology already is used in autonomous vehicles. Plus, one benefit of optical mapping technology is how naturally it translates into an app. Because the Eye’s software knows in real time where it is and where it’s been, it can relay a live activity map to the user’s phone, where it can monitored and remotely programmed. While the Eye doesn’t learn homeowners’ behavior patterns like Nest, it certainly seems like it could later. The infrastructure is already in place.
The Dyson 360 Eye goes on sale next spring, first in Japan and then worldwide. The price is not yet set.
social media trends 2014
social media trends 2014
KEEP IN TOUCH FOR MORE ON MARKETING AND TECHNOLOGY















 Dyson
Dyson
I have found that this site is very informative, interesting and very well written. keep up the nice high quality writing Local Child Care Marketing Sydney
ReplyDelete